Packmol: Create liquids, gases, solid-liquid interfaces¶
This example illustrates various ways of using the packmol interface for constructing liquid or gas mixtures or solid/liquid interfaces.
To follow along, either
Download
PackMol.py(run as$AMSBIN/amspython PackMol.py).Download
PackMol.ipynb(see also: how to install Jupyterlab in AMS)
Worked Example¶
Initial imports¶
from scm.plams import plot_molecule, from_smiles, Molecule
from scm.plams.interfaces.molecule.packmol import packmol
from ase.visualize.plot import plot_atoms
from ase.build import fcc111, bulk
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scm.version import release
AMS2025 = release >= "2024.201"
AMS2026 = release >= "2025.201"
if AMS2025:
from scm.plams import packmol_around
try:
from scm.plams import view # view molecule using AMSview in a Jupyter Notebook in AMS2026+
except ImportError:
from scm.plams import plot_molecule # plot molecule in a Jupyter Notebook in AMS2023+
def view(molecule, **kwargs):
plot_molecule(molecule)
Helper functions¶
def printsummary(mol, details=None):
if details:
density = details["density"]
else:
density = mol.get_density() * 1e-3
s = f"{len(mol)} atoms, density = {density:.3f} g/cm^3"
if mol.lattice:
s += f", box = {mol.lattice[0][0]:.3f}, {mol.lattice[1][1]:.3f}, {mol.lattice[2][2]:.3f}"
s += f", formula = {mol.get_formula()}"
if details:
s += f'\n#added molecules per species: {details["n_molecules"]}, mole fractions: {details["mole_fractions"]}'
print(s)
Liquid water (fluid with 1 component)¶
First, create the gasphase molecule:
water = from_smiles("O")
view(water, width=200, height=200)
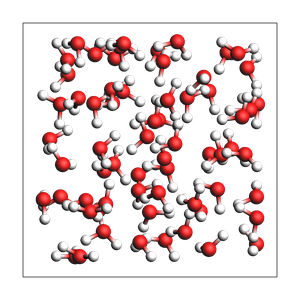
print("pure liquid from approximate number of atoms and exact density (in g/cm^3), cubic box with auto-determined size")
out = packmol(water, n_atoms=194, density=1.0)
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-1.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
pure liquid from approximate number of atoms and exact density (in g/cm^3), cubic box with auto-determined size
195 atoms, density = 1.000 g/cm^3, box = 12.482, 12.482, 12.482, formula = H130O65

print("pure liquid from approximate density (in g/cm^3) and an orthorhombic box")
out = packmol(water, density=1.0, box_bounds=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 8.0, 12.0, 14.0])
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-2.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
pure liquid from approximate density (in g/cm^3) and an orthorhombic box
135 atoms, density = 1.002 g/cm^3, box = 8.000, 12.000, 14.000, formula = H90O45

print("pure liquid with explicit number of molecules and exact density")
out = packmol(water, n_molecules=64, density=1.0)
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-3.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
pure liquid with explicit number of molecules and exact density
192 atoms, density = 1.000 g/cm^3, box = 12.417, 12.417, 12.417, formula = H128O64
print("pure liquid with explicit number of molecules and box")
out = packmol(water, n_molecules=64, box_bounds=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 12.0, 13.0, 14.0])
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-4.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
pure liquid with explicit number of molecules and box
192 atoms, density = 0.877 g/cm^3, box = 12.000, 13.000, 14.000, formula = H128O64

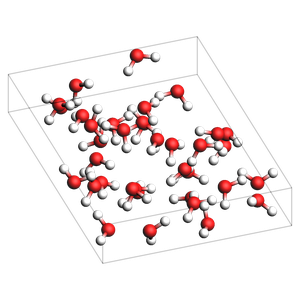
if AMS2025:
print("water-5.xyz: pure liquid in non-orthorhombic box (requires AMS2025 or later)")
print("NOTE: Non-orthorhombic boxes may yield inaccurate results, always carefully check the output")
# You can pack inside any lattice using the packmol_around function
box = Molecule()
box.lattice = [[10.0, 2.0, -1.0], [-5.0, 8.0, 0.0], [0.0, -2.0, 11.0]]
out = packmol_around(box, molecules=[water], n_molecules=[32])
out.write("water-5.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
else:
img = None
img
water-5.xyz: pure liquid in non-orthorhombic box (requires AMS2025 or later)
NOTE: Non-orthorhombic boxes may yield inaccurate results, always carefully check the output
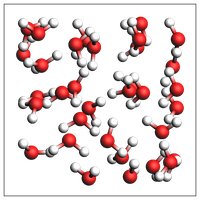
if AMS2025:
print("Experimental feature (AMS2025): guess density for pure liquid")
print("Note: This density is meant to be equilibrated with NPT MD. It can be very inaccurate!")
out = packmol(water, n_atoms=100)
print(f"Guessed density: {out.get_density():.2f} kg/m^3")
img = view(out, width=200, height=200, padding=-2)
else:
img = None
img
Experimental feature (AMS2025): guess density for pure liquid
Note: This density is meant to be equilibrated with NPT MD. It can be very inaccurate!
Guessed density: 1013.97 kg/m^3
Water-acetonitrile mixture (fluid with 2 or more components)¶
Let’s also create a single acetonitrile molecule:
acetonitrile = from_smiles("CC#N")
view(acetonitrile, width=200, height=200)
Set the desired mole fractions and density. Here, the density is calculated as the weighted average of water (1.0 g/cm^3) and acetonitrile (0.76 g/cm^3) densities, but you could use any other density.
# MIXTURES
x_water = 0.666 # mole fraction
x_acetonitrile = 1 - x_water # mole fraction
# weighted average of pure component densities
density = (x_water * 1.0 + x_acetonitrile * 0.76) / (x_water + x_acetonitrile)
print("MIXTURES")
print(f"x_water = {x_water:.3f}")
print(f"x_acetonitrile = {x_acetonitrile:.3f}")
print(f"target density = {density:.3f} g/cm^3")
MIXTURES
x_water = 0.666
x_acetonitrile = 0.334
target density = 0.920 g/cm^3
By setting return_details=True, you can get information about the mole fractions of the returned system. They may not exactly match the mole fractions you put in.
print(
"2-1 water-acetonitrile from approximate number of atoms and exact density (in g/cm^3), "
"cubic box with auto-determined size"
)
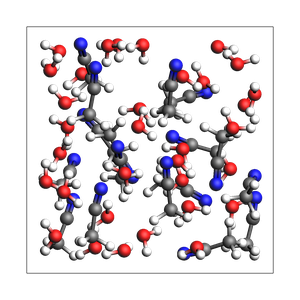
out, details = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile],
n_atoms=200,
density=density,
return_details=True,
)
printsummary(out, details)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-1.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
2-1 water-acetonitrile from approximate number of atoms and exact density (in g/cm^3), cubic box with auto-determined size
201 atoms, density = 0.920 g/cm^3, box = 13.263, 13.263, 13.263, formula = C34H117N17O33
#added molecules per species: [33, 17], mole fractions: [0.66, 0.34]
The details is a dictionary as follows:
for k, v in details.items():
print(f"{k}: {v}")
n_molecules: [33, 17]
mole_fractions: [0.66, 0.34]
n_atoms: 201
molecule_type_indices: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
molecule_indices: [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 13, 13, 13, 14, 14, 14, 15, 15, 15, 16, 16, 16, 17, 17, 17, 18, 18, 18, 19, 19, 19, 20, 20, 20, 21, 21, 21, 22, 22, 22, 23, 23, 23, 24, 24, 24, 25, 25, 25, 26, 26, 26, 27, 27, 27, 28, 28, 28, 29, 29, 29, 30, 30, 30, 31, 31, 31, 32, 32, 32, 33, 33, 33, 33, 33, 33, 34, 34, 34, 34, 34, 34, 35, 35, 35, 35, 35, 35, 36, 36, 36, 36, 36, 36, 37, 37, 37, 37, 37, 37, 38, 38, 38, 38, 38, 38, 39, 39, 39, 39, 39, 39, 40, 40, 40, 40, 40, 40, 41, 41, 41, 41, 41, 41, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 43, 43, 43, 43, 43, 43, 44, 44, 44, 44, 44, 44, 45, 45, 45, 45, 45, 45, 46, 46, 46, 46, 46, 46, 47, 47, 47, 47, 47, 47, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 49, 49, 49, 49, 49, 49]
atom_indices_in_molecule: [0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
volume: 2333.0853879652004
density: 0.9198400000000004
print("2-1 water-acetonitrile from approximate density (in g/cm^3) and box bounds")
out, details = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile],
box_bounds=[0, 0, 0, 13.2, 13.2, 13.2],
density=density,
return_details=True,
)
printsummary(out, details)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-2.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
2-1 water-acetonitrile from approximate density (in g/cm^3) and box bounds
201 atoms, density = 0.933 g/cm^3, box = 13.200, 13.200, 13.200, formula = C34H117N17O33
#added molecules per species: [33, 17], mole fractions: [0.66, 0.34]

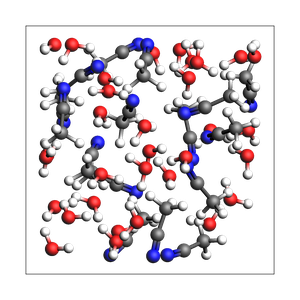
print("2-1 water-acetonitrile from explicit number of molecules and density, cubic box with auto-determined size")
out, details = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
n_molecules=[32, 16],
density=density,
return_details=True,
)
printsummary(out, details)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-3.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
2-1 water-acetonitrile from explicit number of molecules and density, cubic box with auto-determined size
192 atoms, density = 0.920 g/cm^3, box = 13.058, 13.058, 13.058, formula = C32H112N16O32
#added molecules per species: [32, 16], mole fractions: [0.6666666666666666, 0.3333333333333333]
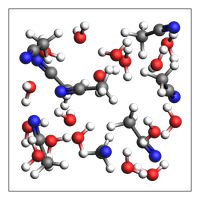
print("2-1 water-acetonitrile from explicit number of molecules and box")
out = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
n_molecules=[32, 16],
box_bounds=[0, 0, 0, 13.2, 13.2, 13.2],
)
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-4.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
2-1 water-acetonitrile from explicit number of molecules and box
192 atoms, density = 0.890 g/cm^3, box = 13.200, 13.200, 13.200, formula = C32H112N16O32

if AMS2025:
print("Experimental feature (AMS2025): guess density for mixture")
print("Note: This density is meant to be equilibrated with NPT MD. It can be very inaccurate!")
out = packmol([water, acetonitrile], mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile], n_atoms=100)
print(f"Guessed density: {out.get_density():.2f} kg/m^3")
img = view(out, width=200, height=200, padding=-2)
else:
img = None
img
Experimental feature (AMS2025): guess density for mixture
Note: This density is meant to be equilibrated with NPT MD. It can be very inaccurate!
Guessed density: 849.35 kg/m^3
NaCl solution (solvent with 1 or more solutes)¶
sodium = from_smiles("[Na+]")
chloride = from_smiles("[Cl-]")
For dilute solutions, it can be useful to specify the number of solute species, and fill up the rest of the box with solvent.
The required number of solvent molecules are then added to fill up the box to the target overall density or number of atoms.
This feature can be used if exactly one of the elements of the n_molecules list is None.
if AMS2026:
print(
"NaCl solution from approximate density (in g/cm^3) and box bounds, and auto-determined number of solvent molecules"
)
out = packmol([sodium, chloride, water], n_molecules=[5, 5, None], density=1.029, box_bounds=[0, 0, 0, 19, 19, 19])
printsummary(out)
out.write("sodium-chloride-solution-1.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3, fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
NaCl solution from approximate density (in g/cm^3) and box bounds, and auto-determined number of solvent molecules
670 atoms, density = 1.030 g/cm^3, box = 19.000, 19.000, 19.000, formula = Cl5H440Na5O220
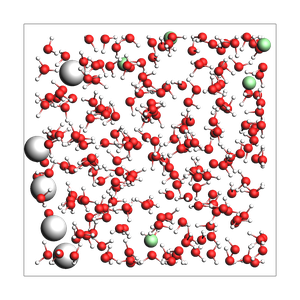
Specify the total number of atoms instead of box bounds, and auto-determine a cubic box:
if AMS2026:
print("NaCl solution from approximate number of atoms and density:")
out = packmol([sodium, chloride, water], n_molecules=[5, 5, None], density=1.029, n_atoms=500)
printsummary(out)
out.write("sodium-chloride-solution-2.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3, fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
NaCl solution from approximate number of atoms and density:
499 atoms, density = 1.029 g/cm^3, box = 17.336, 17.336, 17.336, formula = Cl5H326Na5O163
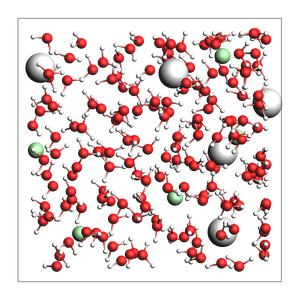
Specify the total number of atoms instead of the density (less useful option):
if AMS2026:
print("NaCl solution from approximate number of atoms and box_bounds:")
out = packmol([sodium, chloride, water], n_molecules=[5, 5, None], n_atoms=500, box_bounds=[0, 0, 0, 12, 18, 24])
printsummary(out)
out.write("sodium-chloride-solution-3.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3, fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
NaCl solution from approximate number of atoms and box_bounds:
499 atoms, density = 1.034 g/cm^3, box = 12.000, 18.000, 24.000, formula = Cl5H326Na5O163
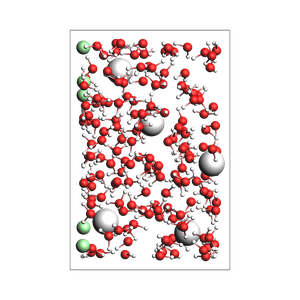
Pack inside sphere¶
Set sphere=True to pack in a sphere (non-periodic) instead of in a periodic box. The sphere will be centered near the origin.
print("water in a sphere from exact density and number of molecules")
out, details = packmol(molecules=[water], n_molecules=[100], density=1.0, return_details=True, sphere=True)
printsummary(out, details)
print(f"Radius of sphere: {details['radius']:.3f} ang.")
print(f"Center of mass xyz (ang): {out.get_center_of_mass()}")
out.write("water-sphere.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3)
water in a sphere from exact density and number of molecules
300 atoms, density = 1.000 g/cm^3, formula = H200O100
#added molecules per species: [100], mole fractions: [1.0]
Radius of sphere: 8.939 ang.
Center of mass xyz (ang): (-0.1699190093953493, 0.09202619949395398, 0.32964314142567197)
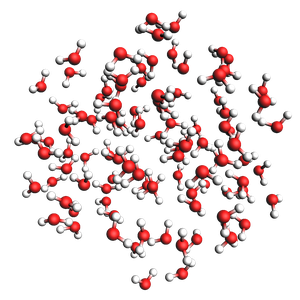
print(
"2-1 water-acetonitrile in a sphere from exact density (in g/cm^3) and "
"approximate number of atoms and mole fractions"
)
out, details = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile],
n_atoms=500,
density=density,
return_details=True,
sphere=True,
)
printsummary(out, details)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-sphere.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3)
2-1 water-acetonitrile in a sphere from exact density (in g/cm^3) and approximate number of atoms and mole fractions
501 atoms, density = 0.920 g/cm^3, formula = C84H292N42O83
#added molecules per species: [83, 42], mole fractions: [0.664, 0.336]

Packing ions, total system charge¶
The total system charge will be sum of the charges of the constituent molecules.
In PLAMS, molecule.properties.charge specifies the charge:
ammonium = from_smiles("[NH4+]") # ammonia.properties.charge == +1
chloride = from_smiles("[Cl-]") # chloride.properties.charge == -1
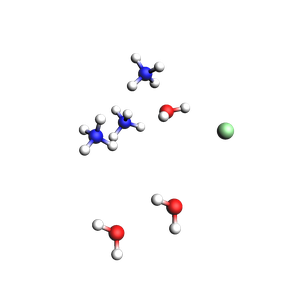
print("3 water molecules, 3 ammonium, 1 chloride (non-periodic)")
print("Initial charges:")
print(f"Water: {water.properties.get('charge', 0)}")
print(f"Ammonium: {ammonium.properties.get('charge', 0)}")
print(f"Chloride: {chloride.properties.get('charge', 0)}")
out = packmol(molecules=[water, ammonium, chloride], n_molecules=[3, 3, 1], density=0.4, sphere=True)
tot_charge = out.properties.get("charge", 0)
print(f"Total charge of packmol-generated system: {tot_charge}")
out.write("water-ammonium-chloride.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300)
3 water molecules, 3 ammonium, 1 chloride (non-periodic)
Initial charges:
Water: 0
Ammonium: 1
Chloride: -1
Total charge of packmol-generated system: 2
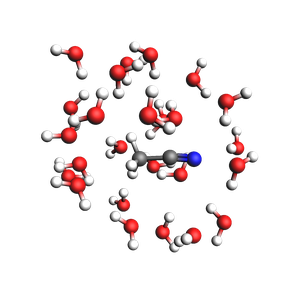
Microsolvation¶
packmol_microsolvation can create a microsolvation sphere around a solute.
from scm.plams import packmol_microsolvation
out = packmol_microsolvation(solute=acetonitrile, solvent=water, density=1.5, threshold=4.0)
# for microsolvation it's a good idea to have a higher density than normal to get enough solvent molecules
print(f"Microsolvated structure: {len(out)} atoms.")
out.write("acetonitrile-microsolvated.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-1)
Microsolvated structure: 81 atoms.
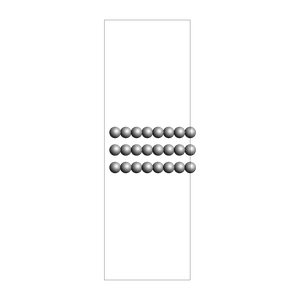
Solid-liquid or solid-gas interfaces¶
First, create a slab using the ASE fcc111 function
from scm.plams import plot_molecule, fromASE
from ase.build import fcc111
rotation = "90x,0y,0z" # sideview of slab
slab = fromASE(fcc111("Al", size=(4, 6, 3), vacuum=15.0, orthogonal=True, periodic=True))
view(slab, width=300, height=300, direction="along_y", fixed_atom_size=False)
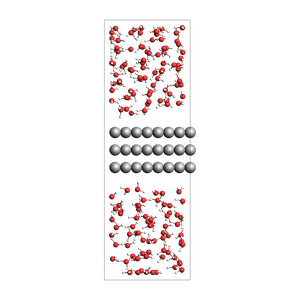
print("water surrounding an Al slab, from an approximate density")
if AMS2025:
out = packmol_around(slab, water, density=1.0)
printsummary(out)
out.write("al-water-pure.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, direction="along_y", fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
water surrounding an Al slab, from an approximate density
534 atoms, density = 1.325 g/cm^3, box = 11.455, 14.881, 34.677, formula = Al72H308O154
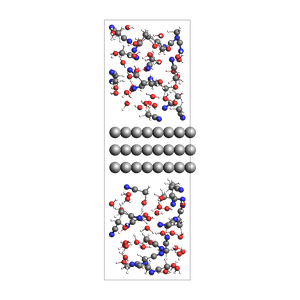
print("2-1 water-acetonitrile mixture surrounding an Al slab, from mole fractions and an approximate density")
if AMS2025:
out = packmol_around(slab, [water, acetonitrile], mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile], density=density)
printsummary(out)
out.write("al-water-acetonitrile.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, direction="along_y", fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
2-1 water-acetonitrile mixture surrounding an Al slab, from mole fractions and an approximate density
468 atoms, density = 1.260 g/cm^3, box = 11.455, 14.881, 34.677, formula = C66H231Al72N33O66
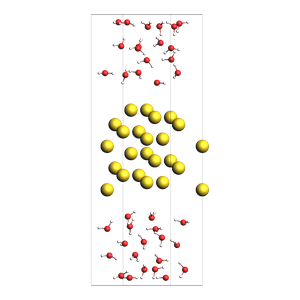
from ase.build import surface
if AMS2025:
print("water surrounding non-orthorhombic Au(211) slab, from an approximate number of molecules")
print("NOTE: non-orthorhombic cell, results are approximate, requires AMS2025")
slab = surface("Au", (2, 1, 1), 6)
slab.center(vacuum=11.0, axis=2)
slab.set_pbc(True)
out = packmol_around(fromASE(slab), [water], n_molecules=[32], tolerance=1.8)
out.write("Au211-water.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, direction="along_y", fixed_atom_size=False)
print(f"{out.lattice=}")
else:
img = None
img
water surrounding non-orthorhombic Au(211) slab, from an approximate number of molecules
NOTE: non-orthorhombic cell, results are approximate, requires AMS2025
out.lattice=[[9.1231573482, 0.0, 0.0], [3.6492629392999993, 4.4694160692, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 31.161091638]]
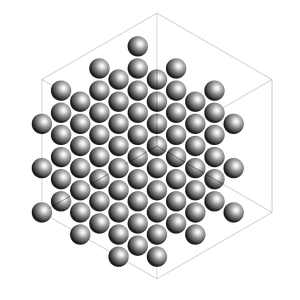
Pack inside voids in crystals¶
Use the packmol_around function. You can decrease tolerance if you need to pack very tightly. The default value for tolerance is 2.0.
from scm.plams import fromASE
from ase.build import bulk
bulk_Al = fromASE(bulk("Al", cubic=True).repeat((3, 3, 3)))
rotation = "-85x,5y,0z"
view(bulk_Al, width=300, height=300, direction="corner_z", fixed_atom_size=False)
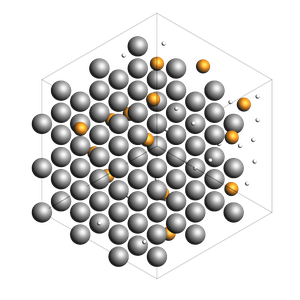
if AMS2025:
out = packmol_around(
current=bulk_Al,
molecules=[from_smiles("[H]"), from_smiles("[He]")],
n_molecules=[50, 20],
tolerance=1.5,
)
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, direction="corner_z", fixed_atom_size=False)
printsummary(out)
out.write("al-bulk-with-h-he.xyz")
else:
img = None
img
178 atoms, density = 2.819 g/cm^3, box = 12.150, 12.150, 12.150, formula = Al108H50He20
Bonds, atom properties (force field types, regions, …)¶
The packmol() function accepts the arguments keep_bonds and keep_atom_properties. These options will keep the bonds defined for the constitutent molecules, as well as any atomic properties.
The bonds and atom properties are easiest to see by printing the System block for an AMS job:
from scm.plams import Settings
water = from_smiles("O")
n2 = from_smiles("N#N")
# delete properties coming from from_smiles
for at in water:
at.properties = Settings()
for at in n2:
at.properties = Settings()
water[1].properties.region = "oxygen_atom"
water[2].properties.mass = 2.014 # deuterium
water.delete_bond(water[1, 2]) # delete bond between atoms 1 and 2 (O and H)
from scm.plams import AMSJob
out = packmol([water, n2], n_molecules=[2, 1], density=0.5)
print(AMSJob(molecule=out).get_input())
System
Atoms
O 4.4441150000 1.4922580000 2.9729990000 region=mol0,oxygen_atom
H 4.9704890000 1.0116830000 3.6459450000 mass=2.014 region=mol0
H 4.9710200000 2.1904030000 2.5267040000 region=mol0
O 2.9752960000 1.7069390000 1.1517670000 region=mol0,oxygen_atom
H 1.9962270000 1.6977940000 1.1046520000 mass=2.014 region=mol0
H 3.3346120000 2.6201090000 1.1167260000 region=mol0
N 2.0005160000 1.0328020000 4.8790080000 region=mol1
N 1.0990030000 1.6791750000 4.9189680000 region=mol1
End
BondOrders
1 3 1.0
4 6 1.0
7 8 3.0
End
Lattice
5.9692549746 0.0000000000 0.0000000000
0.0000000000 5.9692549746 0.0000000000
0.0000000000 0.0000000000 5.9692549746
End
End
By default, the packmol() function assigns regions called mol0, mol1, etc. to the different added molecules. The region_names option lets you set custom names.
out = packmol(
[water, n2],
n_molecules=[2, 1],
density=0.5,
region_names=["water", "nitrogen_molecule"],
)
print(AMSJob(molecule=out).get_input())
System
Atoms
O 4.9620400000 1.6698730000 4.3149830000 region=oxygen_atom,water
H 4.6432870000 2.1842420000 3.5438150000 mass=2.014 region=water
H 4.3116430000 0.9895500000 4.5949130000 region=water
O 2.5512570000 2.5639210000 4.1167190000 region=oxygen_atom,water
H 2.4898890000 1.7287630000 3.6071860000 mass=2.014 region=water
H 1.6871030000 3.0278390000 4.1639800000 region=water
N 4.9510920000 4.3697830000 1.2574330000 region=nitrogen_molecule
N 4.1364110000 5.0022300000 1.6678300000 region=nitrogen_molecule
End
BondOrders
1 3 1.0
4 6 1.0
7 8 3.0
End
Lattice
5.9692549746 0.0000000000 0.0000000000
0.0000000000 5.9692549746 0.0000000000
0.0000000000 0.0000000000 5.9692549746
End
End
Below, we also set keep_atom_properties=False, this will remove the previous regions (in this example “oxygen_atom”) and mass.
out = packmol([water, n2], n_molecules=[2, 1], density=0.5, keep_atom_properties=False)
print(AMSJob(molecule=out).get_input())
System
Atoms
O 4.8024220000 2.4670700000 4.4848050000 region=mol0
H 3.8753180000 2.7822470000 4.4398630000 region=mol0
H 4.8699540000 1.5906950000 4.9225500000 region=mol0
O 1.9212080000 1.8057560000 4.6132510000 region=mol0
H 0.9667180000 1.7779110000 4.8347280000 region=mol0
H 2.1510480000 1.1659660000 3.9046900000 region=mol0
N 5.0598080000 4.6629490000 4.3879830000 region=mol1
N 4.1724870000 4.9830850000 4.9730410000 region=mol1
End
BondOrders
1 3 1.0
4 6 1.0
7 8 3.0
End
Lattice
5.9692549746 0.0000000000 0.0000000000
0.0000000000 5.9692549746 0.0000000000
0.0000000000 0.0000000000 5.9692549746
End
End
keep_bonds=False will additionally ignore any defined bonds:
out = packmol(
[water, n2],
n_molecules=[2, 1],
density=0.5,
region_names=["water", "nitrogen_molecule"],
keep_bonds=False,
keep_atom_properties=False,
)
print(AMSJob(molecule=out).get_input())
System
Atoms
O 1.1645490000 1.9350520000 1.0286860000 region=water
H 1.3546670000 0.9803260000 1.1437180000 region=water
H 1.9874870000 2.4685300000 0.9797960000 region=water
O 3.6891970000 1.1646230000 1.9027560000 region=water
H 3.5118060000 1.9842520000 2.4103190000 region=water
H 4.3178890000 1.3203450000 1.1647090000 region=water
N 1.3013450000 1.1564020000 4.9654650000 region=nitrogen_molecule
N 1.4430920000 1.6175590000 3.9657840000 region=nitrogen_molecule
End
Lattice
5.9692549746 0.0000000000 0.0000000000
0.0000000000 5.9692549746 0.0000000000
0.0000000000 0.0000000000 5.9692549746
End
End
Complete Python code¶
#!/usr/bin/env amspython
# coding: utf-8
# ## Initial imports
from scm.plams import plot_molecule, from_smiles, Molecule
from scm.plams.interfaces.molecule.packmol import packmol
from ase.visualize.plot import plot_atoms
from ase.build import fcc111, bulk
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scm.version import release
AMS2025 = release >= "2024.201"
AMS2026 = release >= "2025.201"
if AMS2025:
from scm.plams import packmol_around
try:
from scm.plams import view # view molecule using AMSview in a Jupyter Notebook in AMS2026+
except ImportError:
from scm.plams import plot_molecule # plot molecule in a Jupyter Notebook in AMS2023+
def view(molecule, **kwargs):
plot_molecule(molecule)
# ## Helper functions
def printsummary(mol, details=None):
if details:
density = details["density"]
else:
density = mol.get_density() * 1e-3
s = f"{len(mol)} atoms, density = {density:.3f} g/cm^3"
if mol.lattice:
s += f", box = {mol.lattice[0][0]:.3f}, {mol.lattice[1][1]:.3f}, {mol.lattice[2][2]:.3f}"
s += f", formula = {mol.get_formula()}"
if details:
s += f'\n#added molecules per species: {details["n_molecules"]}, mole fractions: {details["mole_fractions"]}'
print(s)
# ## Liquid water (fluid with 1 component)
# First, create the gasphase molecule:
water = from_smiles("O")
view(water, width=200, height=200)
print("pure liquid from approximate number of atoms and exact density (in g/cm^3), cubic box with auto-determined size")
out = packmol(water, n_atoms=194, density=1.0)
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-1.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
print("pure liquid from approximate density (in g/cm^3) and an orthorhombic box")
out = packmol(water, density=1.0, box_bounds=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 8.0, 12.0, 14.0])
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-2.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
print("pure liquid with explicit number of molecules and exact density")
out = packmol(water, n_molecules=64, density=1.0)
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-3.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
print("pure liquid with explicit number of molecules and box")
out = packmol(water, n_molecules=64, box_bounds=[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 12.0, 13.0, 14.0])
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-4.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
if AMS2025:
print("water-5.xyz: pure liquid in non-orthorhombic box (requires AMS2025 or later)")
print("NOTE: Non-orthorhombic boxes may yield inaccurate results, always carefully check the output")
# You can pack inside any lattice using the packmol_around function
box = Molecule()
box.lattice = [[10.0, 2.0, -1.0], [-5.0, 8.0, 0.0], [0.0, -2.0, 11.0]]
out = packmol_around(box, molecules=[water], n_molecules=[32])
out.write("water-5.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
else:
img = None
img
if AMS2025:
print("Experimental feature (AMS2025): guess density for pure liquid")
print("Note: This density is meant to be equilibrated with NPT MD. It can be very inaccurate!")
out = packmol(water, n_atoms=100)
print(f"Guessed density: {out.get_density():.2f} kg/m^3")
img = view(out, width=200, height=200, padding=-2)
else:
img = None
img
# ## Water-acetonitrile mixture (fluid with 2 or more components)
# Let's also create a single acetonitrile molecule:
acetonitrile = from_smiles("CC#N")
view(acetonitrile, width=200, height=200)
# Set the desired mole fractions and density. Here, the density is calculated as the weighted average of water (1.0 g/cm^3) and acetonitrile (0.76 g/cm^3) densities, but you could use any other density.
# MIXTURES
x_water = 0.666 # mole fraction
x_acetonitrile = 1 - x_water # mole fraction
# weighted average of pure component densities
density = (x_water * 1.0 + x_acetonitrile * 0.76) / (x_water + x_acetonitrile)
print("MIXTURES")
print(f"x_water = {x_water:.3f}")
print(f"x_acetonitrile = {x_acetonitrile:.3f}")
print(f"target density = {density:.3f} g/cm^3")
# By setting ``return_details=True``, you can get information about the mole fractions of the returned system. They may not exactly match the mole fractions you put in.
print(
"2-1 water-acetonitrile from approximate number of atoms and exact density (in g/cm^3), "
"cubic box with auto-determined size"
)
out, details = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile],
n_atoms=200,
density=density,
return_details=True,
)
printsummary(out, details)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-1.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
# The ``details`` is a dictionary as follows:
for k, v in details.items():
print(f"{k}: {v}")
print("2-1 water-acetonitrile from approximate density (in g/cm^3) and box bounds")
out, details = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile],
box_bounds=[0, 0, 0, 13.2, 13.2, 13.2],
density=density,
return_details=True,
)
printsummary(out, details)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-2.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
print("2-1 water-acetonitrile from explicit number of molecules and density, cubic box with auto-determined size")
out, details = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
n_molecules=[32, 16],
density=density,
return_details=True,
)
printsummary(out, details)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-3.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
print("2-1 water-acetonitrile from explicit number of molecules and box")
out = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
n_molecules=[32, 16],
box_bounds=[0, 0, 0, 13.2, 13.2, 13.2],
)
printsummary(out)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-4.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-2)
if AMS2025:
print("Experimental feature (AMS2025): guess density for mixture")
print("Note: This density is meant to be equilibrated with NPT MD. It can be very inaccurate!")
out = packmol([water, acetonitrile], mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile], n_atoms=100)
print(f"Guessed density: {out.get_density():.2f} kg/m^3")
img = view(out, width=200, height=200, padding=-2)
else:
img = None
img
# ## NaCl solution (solvent with 1 or more solutes)
sodium = from_smiles("[Na+]")
chloride = from_smiles("[Cl-]")
# For dilute solutions, it can be useful to specify the number of solute species, and fill up the rest of the box with solvent.
#
# The required number of solvent molecules are then added to fill up the box to the target overall density or number of atoms.
#
# This feature can be used if exactly **one** of the elements of the ``n_molecules`` list is None.
if AMS2026:
print(
"NaCl solution from approximate density (in g/cm^3) and box bounds, and auto-determined number of solvent molecules"
)
out = packmol([sodium, chloride, water], n_molecules=[5, 5, None], density=1.029, box_bounds=[0, 0, 0, 19, 19, 19])
printsummary(out)
out.write("sodium-chloride-solution-1.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3, fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
# Specify the total number of atoms instead of box bounds, and auto-determine a cubic box:
if AMS2026:
print("NaCl solution from approximate number of atoms and density:")
out = packmol([sodium, chloride, water], n_molecules=[5, 5, None], density=1.029, n_atoms=500)
printsummary(out)
out.write("sodium-chloride-solution-2.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3, fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
# Specify the total number of atoms instead of the density (less useful option):
if AMS2026:
print("NaCl solution from approximate number of atoms and box_bounds:")
out = packmol([sodium, chloride, water], n_molecules=[5, 5, None], n_atoms=500, box_bounds=[0, 0, 0, 12, 18, 24])
printsummary(out)
out.write("sodium-chloride-solution-3.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3, fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
# ## Pack inside sphere
#
# Set ``sphere=True`` to pack in a sphere (non-periodic) instead of in a periodic box. The sphere will be centered near the origin.
print("water in a sphere from exact density and number of molecules")
out, details = packmol(molecules=[water], n_molecules=[100], density=1.0, return_details=True, sphere=True)
printsummary(out, details)
print(f"Radius of sphere: {details['radius']:.3f} ang.")
print(f"Center of mass xyz (ang): {out.get_center_of_mass()}")
out.write("water-sphere.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3)
print(
"2-1 water-acetonitrile in a sphere from exact density (in g/cm^3) and "
"approximate number of atoms and mole fractions"
)
out, details = packmol(
molecules=[water, acetonitrile],
mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile],
n_atoms=500,
density=density,
return_details=True,
sphere=True,
)
printsummary(out, details)
out.write("water-acetonitrile-sphere.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-3)
# ## Packing ions, total system charge
#
# The total system charge will be sum of the charges of the constituent molecules.
#
# In PLAMS, ``molecule.properties.charge`` specifies the charge:
ammonium = from_smiles("[NH4+]") # ammonia.properties.charge == +1
chloride = from_smiles("[Cl-]") # chloride.properties.charge == -1
print("3 water molecules, 3 ammonium, 1 chloride (non-periodic)")
print("Initial charges:")
print(f"Water: {water.properties.get('charge', 0)}")
print(f"Ammonium: {ammonium.properties.get('charge', 0)}")
print(f"Chloride: {chloride.properties.get('charge', 0)}")
out = packmol(molecules=[water, ammonium, chloride], n_molecules=[3, 3, 1], density=0.4, sphere=True)
tot_charge = out.properties.get("charge", 0)
print(f"Total charge of packmol-generated system: {tot_charge}")
out.write("water-ammonium-chloride.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300)
# ## Microsolvation
# ``packmol_microsolvation`` can create a microsolvation sphere around a solute.
from scm.plams import packmol_microsolvation
out = packmol_microsolvation(solute=acetonitrile, solvent=water, density=1.5, threshold=4.0)
# for microsolvation it's a good idea to have a higher density than normal to get enough solvent molecules
print(f"Microsolvated structure: {len(out)} atoms.")
out.write("acetonitrile-microsolvated.xyz")
view(out, width=300, height=300, padding=-1)
# ## Solid-liquid or solid-gas interfaces
# First, create a slab using the ASE ``fcc111`` function
from scm.plams import plot_molecule, fromASE
from ase.build import fcc111
rotation = "90x,0y,0z" # sideview of slab
slab = fromASE(fcc111("Al", size=(4, 6, 3), vacuum=15.0, orthogonal=True, periodic=True))
view(slab, width=300, height=300, direction="along_y", fixed_atom_size=False)
print("water surrounding an Al slab, from an approximate density")
if AMS2025:
out = packmol_around(slab, water, density=1.0)
printsummary(out)
out.write("al-water-pure.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, direction="along_y", fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
print("2-1 water-acetonitrile mixture surrounding an Al slab, from mole fractions and an approximate density")
if AMS2025:
out = packmol_around(slab, [water, acetonitrile], mole_fractions=[x_water, x_acetonitrile], density=density)
printsummary(out)
out.write("al-water-acetonitrile.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, direction="along_y", fixed_atom_size=False)
else:
img = None
img
from ase.build import surface
if AMS2025:
print("water surrounding non-orthorhombic Au(211) slab, from an approximate number of molecules")
print("NOTE: non-orthorhombic cell, results are approximate, requires AMS2025")
slab = surface("Au", (2, 1, 1), 6)
slab.center(vacuum=11.0, axis=2)
slab.set_pbc(True)
out = packmol_around(fromASE(slab), [water], n_molecules=[32], tolerance=1.8)
out.write("Au211-water.xyz")
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, direction="along_y", fixed_atom_size=False)
print(f"{out.lattice=}")
else:
img = None
img
# ## Pack inside voids in crystals
#
# Use the ``packmol_around`` function. You can decrease ``tolerance`` if you need to pack very tightly. The default value for ``tolerance`` is 2.0.
from scm.plams import fromASE
from ase.build import bulk
bulk_Al = fromASE(bulk("Al", cubic=True).repeat((3, 3, 3)))
rotation = "-85x,5y,0z"
view(bulk_Al, width=300, height=300, direction="corner_z", fixed_atom_size=False)
if AMS2025:
out = packmol_around(
current=bulk_Al,
molecules=[from_smiles("[H]"), from_smiles("[He]")],
n_molecules=[50, 20],
tolerance=1.5,
)
img = view(out, width=300, height=300, direction="corner_z", fixed_atom_size=False)
printsummary(out)
out.write("al-bulk-with-h-he.xyz")
else:
img = None
img
# ## Bonds, atom properties (force field types, regions, ...)
#
# The ``packmol()`` function accepts the arguments ``keep_bonds`` and ``keep_atom_properties``. These options will keep the bonds defined for the constitutent molecules, as well as any atomic properties.
#
# The bonds and atom properties are easiest to see by printing the System block for an AMS job:
from scm.plams import Settings
water = from_smiles("O")
n2 = from_smiles("N#N")
# delete properties coming from from_smiles
for at in water:
at.properties = Settings()
for at in n2:
at.properties = Settings()
water[1].properties.region = "oxygen_atom"
water[2].properties.mass = 2.014 # deuterium
water.delete_bond(water[1, 2]) # delete bond between atoms 1 and 2 (O and H)
from scm.plams import AMSJob
out = packmol([water, n2], n_molecules=[2, 1], density=0.5)
print(AMSJob(molecule=out).get_input())
# By default, the ``packmol()`` function assigns regions called ``mol0``, ``mol1``, etc. to the different added molecules. The ``region_names`` option lets you set custom names.
out = packmol(
[water, n2],
n_molecules=[2, 1],
density=0.5,
region_names=["water", "nitrogen_molecule"],
)
print(AMSJob(molecule=out).get_input())
# Below, we also set ``keep_atom_properties=False``, this will remove the previous regions (in this example "oxygen_atom") and mass.
out = packmol([water, n2], n_molecules=[2, 1], density=0.5, keep_atom_properties=False)
print(AMSJob(molecule=out).get_input())
# ``keep_bonds=False`` will additionally ignore any defined bonds:
out = packmol(
[water, n2],
n_molecules=[2, 1],
density=0.5,
region_names=["water", "nitrogen_molecule"],
keep_bonds=False,
keep_atom_properties=False,
)
print(AMSJob(molecule=out).get_input())