Screening industrial polymers for lithium–ion batteries electrode materials
Organic polymers are promising electrode materials for lithium ion batteries due to their low solubility, low self-discharge rates, high mechanical strength, great flexibility, superior thermal stability, and versatility. A recent study virtually screens industrial polymers for their use in Li ion batteries. First, a linear relationship was found between experimental potential and the energy difference between the bare and lithiated polymers (ΔEpoly).
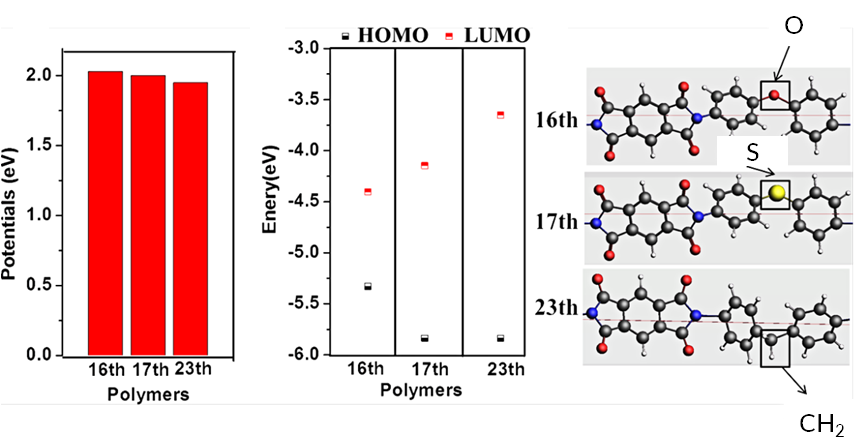
Then 26 industrial polymers were screened on their band gap, theoretical capacity and their predicted potential. The polymers were treated as 1D periodic systems with a polarizable continuum. Three ideal candidates were selected with high potential and high theoretical capacity. The best polymers differ in only one place (O, S or CH2) and the electronegativity of that group is seen to correlate with a lower LUMO and higher potential, which could further help to design novel polymer electrode materials.
H. Lu, J. Yu, G. Chen, and S. Sun, Theoretical screening of novel electrode materials for lithium–ion
batteries from industrial polymers, Ionics (2019)