H-NMR spectrum with spin-spin coupling¶
See also: Corresponding GUI tutorial
In this Python example, you will learn
how to set up an NMR calculation,
how to extract basic results
The example follows the start of the GUI tutorial. See that tutorial for more information.
If you use the GUI, you can see what the inputs to the CPL and NMR programs look like on the Details → Run script panel.
The AMSspectra GUI module contains many functions for analyzing NMR spectra. We recommmend to use it for the analysis. This Python example focuses mainly on running the calculation.
To follow along, either
Download
H-NMRSpinSpinCoupling.py(run as$AMSBIN/amspython H-NMRSpinSpinCoupling.py).Download
H-NMRSpinSpinCoupling.ipynb(see also: how to install Jupyterlab in AMS)
Worked Example¶
Initial imports¶
from scm.base import ChemicalSystem
from scm.plams import AMSJob, Settings, view
System¶
cs = ChemicalSystem(
"""
System
Atoms
O 1.48603879 -1.49561627 0.0
C 1.29751002 -0.30552432 0.0
O 0.07403584000000001 0.25228979 0.0
C -1.02449892 -0.67494471 0.0
C -2.30056502 0.12358769 0.0
C 2.36905363 0.74347075 0.0
H -0.9418758699999999 -1.31519741 0.88039373
H -0.9418758699999999 -1.31519741 -0.88039373
H -2.36617127 0.7582087199999999 0.88525259
H -3.15628689 -0.55419212 0.0
H -2.36617127 0.7582087199999999 -0.88525259
H 3.34355252 0.26293272 0.0
H 2.26362714 1.38098693 0.87932777
H 2.26362714 1.38098693 -0.87932777
End
End
"""
)
# visualize system with bonds
cs_with_bonds = cs.copy()
cs_with_bonds.guess_bonds()
view(cs_with_bonds)
Job settings: DFT and NMR¶
There are three calculations:
A DFT calculation with a main results file
adf.rkf. We must set theSave TAPE10input option. TheTAPE10file is later used by the$AMSBIN/nmrprogram.An
$AMSBIN/cplcalculation. This program modifiesadf.rkfAn
$AMSBIN/nmrcalculation. This program readsTAPE10and modifiesadf.rkf.
In the end, all results are stored on adf.rkf.
There is no PLAMS job for the $AMSBIN/cpl and $AMSBIN/nmr programs. Instead, we set up the calculation explicitly in the settings.runscript.postamble_lines option.
# DFT Settings
s = Settings()
s.input.ams.Task = "SinglePoint"
s.input.adf.Basis.Type = "TZ2P-J"
s.input.adf.Basis.Core = "None"
s.input.adf.Save = "TAPE10"
s.input.adf.xc.GGA = "OPBE"
s.input.adf.Symmetry = "NOSYM"
s.input.adf.NumericalQuality = "Good"
from typing import Mapping, List
def get_cpl_script(s: Mapping) -> List[str]:
ret = (
['"$AMSBIN/cpl" <<eor']
+ ["ADFFile adf.rkf"]
+ ["NMRCOUPLING"]
+ [f" {k} {v}" for k, v in s.items()]
+ ["END"]
+ ["eor"]
+ [""]
)
return ret
def get_nmr_script(s: Mapping) -> List[str]:
ret = (
['"$AMSBIN/nmr" <<eor']
+ ["ADFFile adf.rkf", "TAPE10File TAPE10"]
+ ["NMR"]
+ [f" {k} {v}" for k, v in s.items()]
+ ["End"]
+ ["eor"]
+ [""]
)
return ret
cpl_settings = dict(RespAllAtomsOfType="H", PertAllAtomsOfType="H", fc="", ADFGUI="")
nmr_settings = dict(out="", adfgui="", AllAtomsOfType="H", u1k="best", calc="all")
s.runscript.postamble_lines = get_cpl_script(cpl_settings) + get_nmr_script(nmr_settings)
Inspect the job¶
job = AMSJob(settings=s, molecule=cs, name="ethyl_acetate_nmr")
print(job.get_input()) # DFT settings in the normal input (ethyl_acetate_nmr.in)
Task SinglePoint
System
Atoms
O 1.48603879 -1.4956162699999997 0
C 1.29751002 -0.30552432 0
O 0.07403583999999999 0.25228979 0
C -1.02449892 -0.67494471 0
C -2.30056502 0.12358769 0
C 2.36905363 0.74347075 0
H -0.94187587 -1.31519741 0.88039373
H -0.94187587 -1.31519741 -0.88039373
H -2.36617127 0.75820872 0.88525259
H -3.15628689 -0.55419212 0
H -2.36617127 0.75820872 -0.88525259
H 3.34355252 0.26293272 0
H 2.26362714 1.38098693 0.87932777
H 2.26362714 1.38098693 -0.87932777
End
End
Engine adf
Basis
Core None
Type TZ2P-J
End
NumericalQuality Good
Save TAPE10
Symmetry NOSYM
xc
GGA OPBE
End
EndEngine
print(job.get_runscript()) # post-processing utilities in the runscript
unset AMS_SWITCH_LOGFILE_AND_STDOUT
unset SCM_LOGFILE
AMS_JOBNAME="ethyl_acetate_nmr" AMS_RESULTSDIR=. $AMSBIN/ams --input="ethyl_acetate_nmr.in" < /dev/null
"$AMSBIN/cpl" <<eor
ADFFile adf.rkf
NMRCOUPLING
RespAllAtomsOfType H
PertAllAtomsOfType H
fc
ADFGUI
END
eor
"$AMSBIN/nmr" <<eor
ADFFile adf.rkf
TAPE10File TAPE10
NMR
out
adfgui
AllAtomsOfType H
u1k best
calc all
End
eor
job.run();
[16.12|15:44:51] JOB ethyl_acetate_nmr STARTED
[16.12|15:44:51] JOB ethyl_acetate_nmr RUNNING
[16.12|15:51:33] JOB ethyl_acetate_nmr FINISHED
[16.12|15:51:33] JOB ethyl_acetate_nmr SUCCESSFUL
Results (basic)¶
Let’s see which NMR results are available on adf.rkf:
# job = AMSJob.load_external("/path/to/adf.rkf") # to load a previous job
props = job.results.get_engine_properties()
nmr_keys = [x for x in props.keys() if "NMR" in x]
print(nmr_keys)
['NMR Coupling J tens InputOrder', 'NMR Coupling K tens InputOrder', 'NMR Coupling K const InputOrder', 'NMR Coupling J const InputOrder', 'NMR Shielding Tensor InputOrder', 'NMR Shieldings InputOrder']
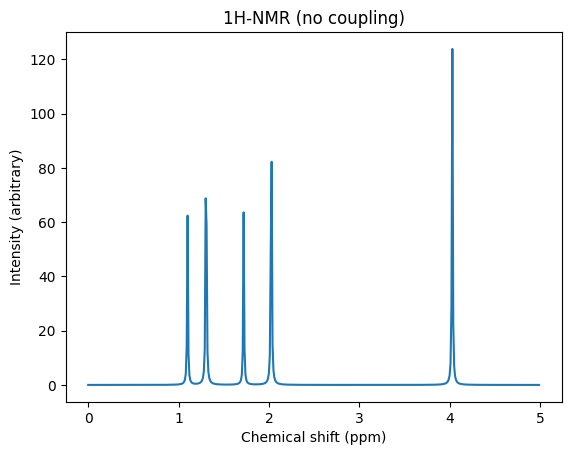
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scm.plams.tools.postprocess_results import broaden_results
sigma_ref_h = 31.7
shieldings = np.array(props["NMR Shieldings InputOrder"])
chemical_shifts = sigma_ref_h - np.array(shieldings)
x, y = broaden_results(
chemical_shifts,
areas=np.ones(chemical_shifts.shape), # weigh all peaks equally
broadening_width=0.01,
broadening_type="lorentzian",
x_data=(0, 5, 0.01), # x range and resolution
)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_title("1H-NMR (no coupling)")
ax.set_xlabel("Chemical shift (ppm)")
ax.set_ylabel("Intensity (arbitrary)")
ax.plot(x, y);
Conclusion¶
In this Python example you learned how to set up and run the NMR calculation.
For more detailed analysis, including multiplet splitting (coupling), see the GUI tutorial.
Recommendation: Use AMSspectra for further analysis.
Complete Python code¶
#!/usr/bin/env amspython
# coding: utf-8
# ## Initial imports
from scm.base import ChemicalSystem
from scm.plams import AMSJob, Settings, view
# ## System
cs = ChemicalSystem(
"""
System
Atoms
O 1.48603879 -1.49561627 0.0
C 1.29751002 -0.30552432 0.0
O 0.07403584000000001 0.25228979 0.0
C -1.02449892 -0.67494471 0.0
C -2.30056502 0.12358769 0.0
C 2.36905363 0.74347075 0.0
H -0.9418758699999999 -1.31519741 0.88039373
H -0.9418758699999999 -1.31519741 -0.88039373
H -2.36617127 0.7582087199999999 0.88525259
H -3.15628689 -0.55419212 0.0
H -2.36617127 0.7582087199999999 -0.88525259
H 3.34355252 0.26293272 0.0
H 2.26362714 1.38098693 0.87932777
H 2.26362714 1.38098693 -0.87932777
End
End
"""
)
# visualize system with bonds
cs_with_bonds = cs.copy()
cs_with_bonds.guess_bonds()
view(cs_with_bonds)
# ## Job settings: DFT and NMR
#
# There are three calculations:
#
# 1. A DFT calculation with a main results file ``adf.rkf``. We must set the ``Save TAPE10`` input option. The ``TAPE10`` file is later used by the ``$AMSBIN/nmr`` program.
#
# 2. An ``$AMSBIN/cpl`` calculation. This program *modifies* ``adf.rkf``
#
# 3. An ``$AMSBIN/nmr`` calculation. This program reads ``TAPE10`` and *modifies* ``adf.rkf``.
#
# In the end, all results are stored on ``adf.rkf``.
#
# There is no PLAMS job for the ``$AMSBIN/cpl`` and ``$AMSBIN/nmr`` programs. Instead, we set up the calculation explicitly in the ``settings.runscript.postamble_lines`` option.
# DFT Settings
s = Settings()
s.input.ams.Task = "SinglePoint"
s.input.adf.Basis.Type = "TZ2P-J"
s.input.adf.Basis.Core = "None"
s.input.adf.Save = "TAPE10"
s.input.adf.xc.GGA = "OPBE"
s.input.adf.Symmetry = "NOSYM"
s.input.adf.NumericalQuality = "Good"
from typing import Mapping, List
def get_cpl_script(s: Mapping) -> List[str]:
ret = (
['"$AMSBIN/cpl" <<eor']
+ ["ADFFile adf.rkf"]
+ ["NMRCOUPLING"]
+ [f" {k} {v}" for k, v in s.items()]
+ ["END"]
+ ["eor"]
+ [""]
)
return ret
def get_nmr_script(s: Mapping) -> List[str]:
ret = (
['"$AMSBIN/nmr" <<eor']
+ ["ADFFile adf.rkf", "TAPE10File TAPE10"]
+ ["NMR"]
+ [f" {k} {v}" for k, v in s.items()]
+ ["End"]
+ ["eor"]
+ [""]
)
return ret
cpl_settings = dict(RespAllAtomsOfType="H", PertAllAtomsOfType="H", fc="", ADFGUI="")
nmr_settings = dict(out="", adfgui="", AllAtomsOfType="H", u1k="best", calc="all")
s.runscript.postamble_lines = get_cpl_script(cpl_settings) + get_nmr_script(nmr_settings)
# ## Inspect the job
job = AMSJob(settings=s, molecule=cs, name="ethyl_acetate_nmr")
print(job.get_input()) # DFT settings in the normal input (ethyl_acetate_nmr.in)
print(job.get_runscript()) # post-processing utilities in the runscript
job.run()
# ## Results (basic)
#
# Let's see which NMR results are available on adf.rkf:
# job = AMSJob.load_external("/path/to/adf.rkf") # to load a previous job
props = job.results.get_engine_properties()
nmr_keys = [x for x in props.keys() if "NMR" in x]
print(nmr_keys)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scm.plams.tools.postprocess_results import broaden_results
sigma_ref_h = 31.7
shieldings = np.array(props["NMR Shieldings InputOrder"])
chemical_shifts = sigma_ref_h - np.array(shieldings)
x, y = broaden_results(
chemical_shifts,
areas=np.ones(chemical_shifts.shape), # weigh all peaks equally
broadening_width=0.01,
broadening_type="lorentzian",
x_data=(0, 5, 0.01), # x range and resolution
)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.set_title("1H-NMR (no coupling)")
ax.set_xlabel("Chemical shift (ppm)")
ax.set_ylabel("Intensity (arbitrary)")
ax.plot(x, y)
# ## Conclusion
#
# In this Python example you learned how to set up and run the NMR calculation.
#
# For more detailed analysis, including multiplet splitting (coupling), see the GUI tutorial.
#
# **Recommendation**: Use AMSspectra for further analysis.