Fukui Functions and the Dual Descriptor¶
Chemical reactivity can be analyzed using Fukui Functions and the Dual Descriptor. ADF provides the tools to perform this analysis. The local chemical reactivity can be described per atom via a condensed Fukui Function. Subsequently, the local softness can be determined as well. The Fukui Functions and the Dual Descriptor can be visualized in the GUI with AMSview.
Step 1: Setting up the calculation¶
 panel active.
panel active.
Here you can specify which Fukui functions you want to calculate. Both can be calculated at the same time, and is also required for the Dual Descriptor. The default way to calculate the Fukui functions is to add or subtract a whole electron. However, it is possible to use fractional charges by modifying the Charge change parameter.
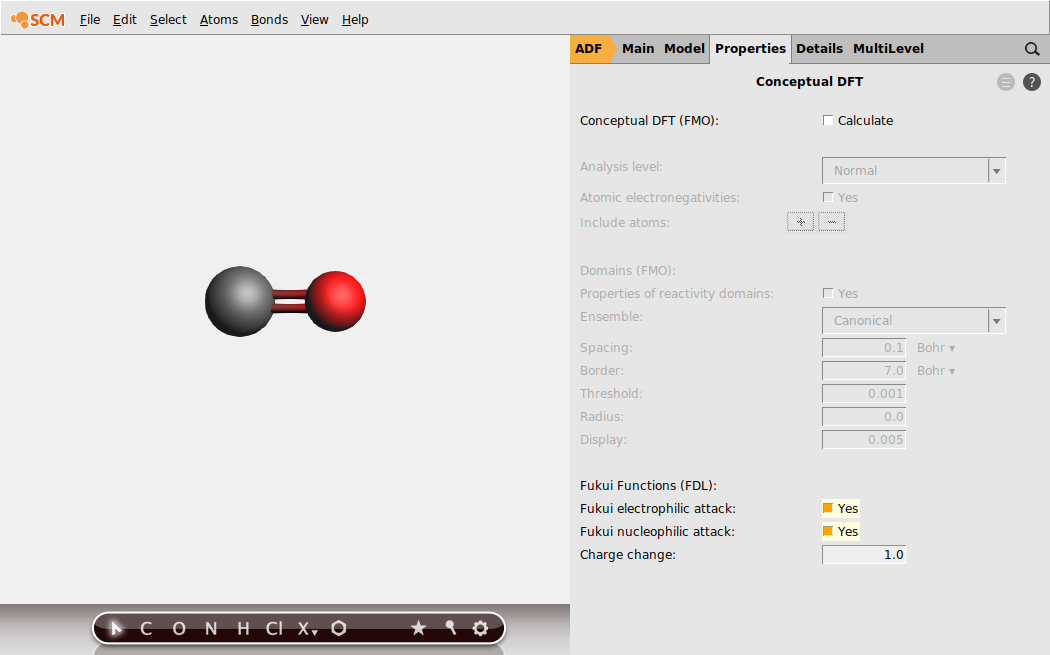
The condensed Fukui Functions and local softness are calculated using atomic charges. By default the Hirshfeld, Voronoi and Mulliken charges are used. The Bader charges can be used as well if they are calculated.
Step 2: The output¶
The condensed Fukui Functions and the local softness can be found in the output file of the main calculation.
Hirshfeld Partitioning
MAIN ATOMIC DESCRIPTORS: CANONICAL ENSEMBLE
===========================================
Atom f+ f- f0 f(2)
C(1) 0.670 0.674 0.672 -0.004
O(2) 0.330 0.326 0.328 0.004
-------------------------------------
Total 1.000 1.000 1.000 -0.000
The condensed Fukui functions are given per atom, with the various atomic charge methods. The above results are for the Hirshfeld partitioning.
Step 3: Visualizing the Fukui functions and Dual Descriptor¶
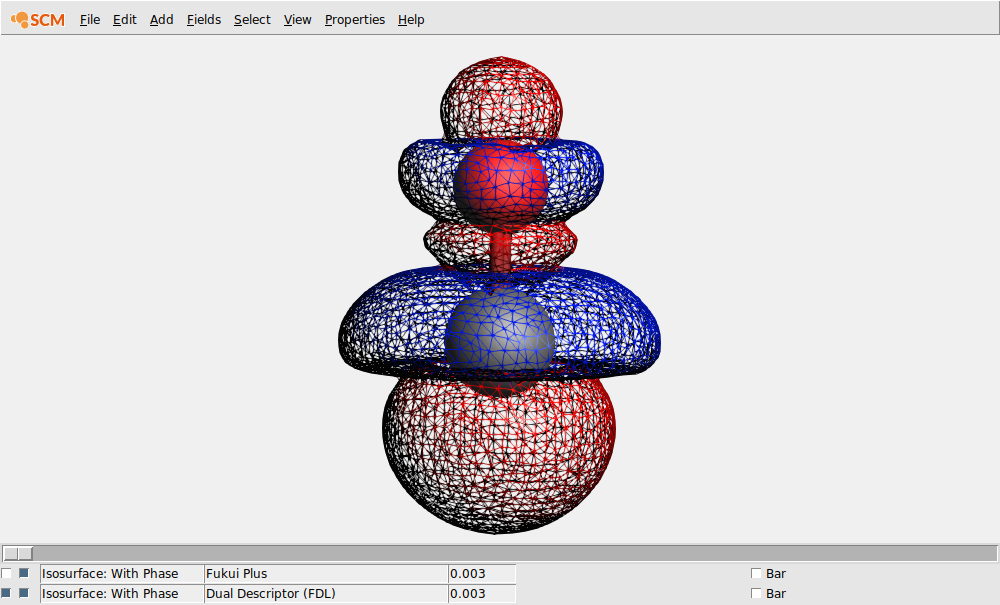
The Fukui functions can be visualized in AMSview, using the electron density.
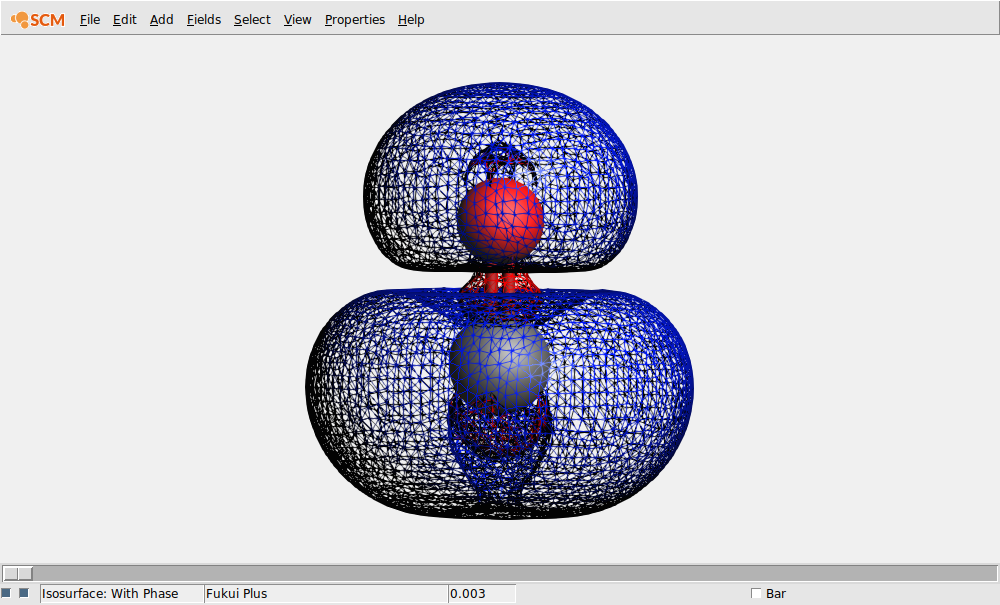
AMSview will create some calculated fields to combine the spin densities for the unrestricted calculations, and calculates the Fukui plus function. The wireframe model allows us to see any hidden isosurface. Another way to do this is by lowering the opacity in the field details.